What is a dental bridge?
A bridge, in dentistry, is also known as a fixed partial denture. It connects three or more crowns in a row, resembling a bridge with landmass on either side. The primary purpose of a bridge is to replace a missing tooth. However, the longer the span of the bridge, the more the forces it has to handle, which can reduce its longevity.
What's the difference between a bridge and dentures?
A bridge is a fixed structure that is cemented in the mouth like a crown and is not removable. On the other hand, a denture or a removable partial denture, which is also used to replace multiple missing teeth, is removable.
What are some of the pros and cons of bridges?
Pros of bridges include their quick completion and cost, which is roughly the same as an implant. They are also suitable if you're not a candidate for dental surgery. However, patients often choose bridges primarily due to their speed, as the procedure can be completed in two visits.
What are the different types of bridges?
Bridges are typically made with teeth on either side, and each tooth is prepared for a full crown. Alternatively, a Maryland bridge or a bonded bridge can be done, where little fins or veneers on the backside of the teeth hold the middle tooth. This type of bridge has the advantage of not requiring crowning of the teeth on either side.
What are some of the alternatives to a bridge?
Implants are the primary alternative to a bridge. Another alternative could be a removable partial denture.
What is a removable bridge and what is a fixed bridge?
A fixed bridge is cemented in the mouth, whereas a removable bridge, also referred to as a removable partial denture, can be taken in and out of the mouth and replaces multiple teeth.
What is a cantilever bridge?
A cantilever bridge is one where the pressure is on one side and an anchor on the other, much like a diving board. This type of bridge is not typically indicated in dentistry, however, there are some situations where it might be used.
Can a bridge help with gum disease?
No, bridges can actually make you more prone to gum disease or periodontal disease as they are harder to clean. Splinting the teeth can be beneficial for periodontal health. This procedure is typically carried out using a wire bonded to the teeth, although other bonding methods are also possible. It's important to note that a dental bridge is not typically considered a means to strengthen or reinforce teeth. This is because a bridge places the force of additional teeth onto the remaining teeth on either side, potentially leading to periodontal complications, gum disease, and weakening of the teeth. These are some of the main disadvantages of using a bridge, and reasons why I might recommend a dental implant instead. However, teeth can be splinted to reinforce them, and this is usually done in various ways.
Is bridge work painful?
In our office, we ensure you are totally numb before we start working on you. So, a bridge procedure would be very similar to a crown or filling appointment. We also provide laughing gas in the office and can give you Valium or Xanax to help you relax.
What is a bridge procedure like?
After numbing the area, we prepare the teeth on either side, and then take a digital scan. That scan is sent to the lab to make the bridge. In the meantime, we will make a temporary bridge for you. The final bridge is typically delivered in two weeks.
How long does a bridge last?
Like anything else, the longevity of dental work depends on how well it is maintained. A major downside of a dental bridge is that it typically does not last as long as an implant. For individuals under 60 without medical contraindications, I would recommend getting an implant, as a bridge is unlikely to last a lifetime. Eventually, the bridge will need replacement, and at that point, its cumulative cost will have exceeded that of an implant. Additionally, the maintenance costs of a bridge are higher.
The lifespan of a bridge is limited partly because it involves splinting three or more teeth together. The longer the span of the bridge, the more stress it endures, increasing the likelihood of breakage, chipping, or loosening. If any issue arises with the bridge, such as chipping or decay under the edges, the entire bridge must be replaced. Therefore, the maintenance costs of a bridge are higher, which is a primary reason I recommend dental implants to my patients.
The average lifespan of a bridge in the United States is about five years, though with good home care and regular maintenance, it could last three times as long. The key to prolonging the life of any dental work, including bridges, is effective cleaning and regular fluoride application. The better the care and maintenance, the longer the dental work is likely to last.
How should I care for my bridge?
When I provide a dental bridge in my office, I also supply all the necessary home care tools to help maintain it properly. These tools include specialized picks designed to clean underneath the bridge. Additionally, there are floss threaders that help in sliding floss under the bridge for thorough cleaning. Another useful tool is super floss, which is a thicker, yarn-like floss specifically designed for cleaning under bridges and other dental work.
However, I recognize that using these tools can be tedious and time-consuming. While they are effective, I've found that people are more likely to engage in regular oral hygiene if the process is easier. Therefore, for patients who receive a bridge at my office, I always recommend using a water flosser or an air-water flosser. These devices use pulses of water or air and water to clean underneath the bridge. It's crucial to clean under the bridge, whether that's done by meticulously flossing underneath or using a water flosser. The key is to choose a method that is both effective and convenient, encouraging consistent dental hygiene practices.
When should I schedule an appointment for a bridge?
There's no bad time to schedule an appointment or a consultation. If you have any questions about replacing a missing tooth, you can call us at (703) 451-4500.
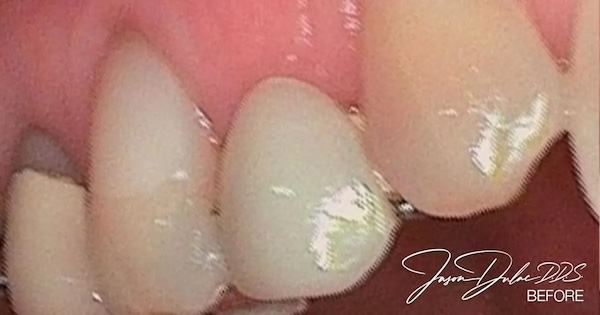
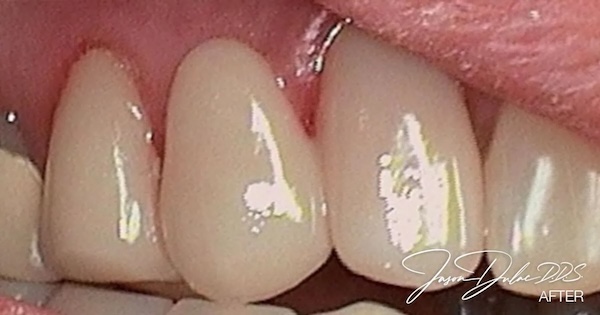
Before & After:
Our patient had a failing bridge on the front upper right and didn’t feel that implants were the right option for her. We removed the old failing bridge and made her a new one that was much more attractive and really helped her smile with more confidence.